

| |
+91-9419178116 (WhatsApp) |
| |

Ladakh maps
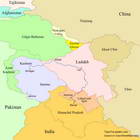 The present day Ladakh is the northernmost administrative division of India. Having been a region of the Jammu and Kasmir state until August 2019, now Ladakh is a union territory of India, governed directly by the Central Government of India.
The present day Ladakh is the northernmost administrative division of India. Having been a region of the Jammu and Kasmir state until August 2019, now Ladakh is a union territory of India, governed directly by the Central Government of India.
On the southwest, Ladakh is separated from the Jammu and Kashmir union territory by the Great Himalayan Range.
On the south, Ladakh borders the district of Lahaul and Spiti of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
On the east, Ladakh borders Tibet and Xinjiang regions of China, including the disputed Aksai Chin area controlled by China. A large part of the boundary between Ladakh and China passes along the demarcation "Line of Actual Control".
On the northwest, along the military "Line of Control", Ladakh borders Baltistan region, which is a part of the disputed Northern Areas (also known as Gilgit-Baltistan) controlled by Pakistan.
On the far north, Ladakh includes Siachen Glacier, the main source of the Nubra River. The disputed area of the Siachen Glacier is controlled by India and borders both Pakistan and China.

|
There are two major ground routes to Ladakh: Manali–Leh and Srinagar–Leh highways.
Srinagar–Leh highway enters Ladakh at Zoji La pass (3528 m) across the Great Himalayan Range. The highway connects Ladakh with Kashmir valley. The highest elevation point of the highway is 4100 m at Fotu La pass. The total length of the highway is considered to be about 434 km (395 km according to Google Earth data). Due to snowfall at the high mountain passes the highway is closed from November–December up to mid-May. The highway is used by the Indian Army as the primary road connecting Ladakh with the rest of the country and it remains open for a longer duration (about 6 months in a year) than the Manali–Leh highway. The current status of the road can be tracked on the official website of the Leh district.

Manali–Leh highway enters Ladakh at Sarchu shortly after Baralacha La pass (4900 m) located in the Great Himalayan Range. The highway connects Ladakh with Himachal Pradesh. The highest elevation point of the highway is 5335 m at Tanglang La pass. The total length of the highway is considered to be 479 km (425 km according to Google Earth data). The highway operates only about four and a half months in a year. Due to snowfall at the high mountain passes the highway is closed from about mid-October to May–June. The current status of the road can be tracked on the official website of the Leh district.

There are several trekking routes connecting Ladakh with other regions. Zanskar valley of Ladakh can be reached through the passes Kang La (5440 m) and the popular Shingo La (5040 m) from the Lahaul valley (Himachal Pradesh). Zanskar can also be reached through the passes Umasi La (5300 m), Poat La (5470 m) and Hagshu La (5030 m) from the Kishtwar valley (Jammu, J&K).
The Rupshu valley of Ladakh and Tso Moriri Lake can be reached through the pass Parang La (5570 m) from the Spiti valley (Himachal Pradesh).
In previous centuries, before the boundary demarcation between India, China and Pakistan, there was an ancient caravan route through the passes Sasser La and Karakoram La connecting the far north of Ladakh and Yarkand, a town lied on the southern branch of the Silk Road. At present, Karakoram La is situated between Ladakh and Xinjiang (China) and remains closed to all traffic. Other historically important routes between Ladakh and Western Tibet including the passes Kongka La, Lanak La (now in Aksai Chin) and Spanggur gap are also currently inaccessible.